Optimal brain function translates into better memory recall, attention span, improved communication skills, and aids in the performance of complex tasks.
Brain health is important at any age, and keeping the brain at peak performance requires the right set of nutrients. Essential nutrients are key players in improving blood flow to the brain and optimizing cognition.* The nutrient citicoline and the common fruit, blueberry, both provide vital compounds that can have a positive impact.*
Citicoline and How it Can Benefit Brain Health*
Citicoline, also known as cytidine-5-diphosphocholine, CDP-choline in supplemental form, is a phospholipid intermediate found in every cell of the body. Citicoline helps to build cell membranes, balances neurotransmitter communication, and provides protective coatings around nerves.* Because of its role in mitochondrial and cell membrane repair, it helps safeguard the nervous system from oxidative stress and age-related damage. 1*
CDP-choline is made up of two principal components, cytidine and choline. These compounds disperse rapidly through the body and cross the blood-brain barrier, targeting the brain. It is part of the phospholipid structure of neuronal membranes. This phospholipid layer is a significant structural component of the cells, which helps to keep them stable. When membranes surrounding neurons and brain cells are more stable, they become more resistant to free radical damage.
Another benefit of citicoline is it increases cerebral metabolism impacting neurotransmitters. Citicoline helps to boost the function of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine, one of the most abundant neurotransmitters in the body.* Found both in the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system, it’s responsible for muscle contraction, regulates endocrine functions, and plays a vital role in memory storage and cognition. Citicoline’s role in neurotransmitter function helps to keep many of the body’s processes running smoothly.*
As cognition tends to decline with age naturally, citicoline may help to improve memory. 2* Its role in membrane maintenance and repair may help to improve blood flow. Citicoline’s impact on nerves in the brain and spinal cord may support benefits to eye health, promoting better function to the optic nerve.3*
Choline, a component of citicoline, is an essential nutrient we only receive from our diet. It’s found naturally in foods such as organ meats, eggs, chicken, fish, and to a lesser extent, in some plant-based foods such as cauliflower and broccoli.
Although choline exists in many foods, it’s richest sources tend to be organ-based meats, which are not common in the American diet. If adequate consumption of choline can’t be established via diet alone, supplemental citicoline may be used to increase its levels.

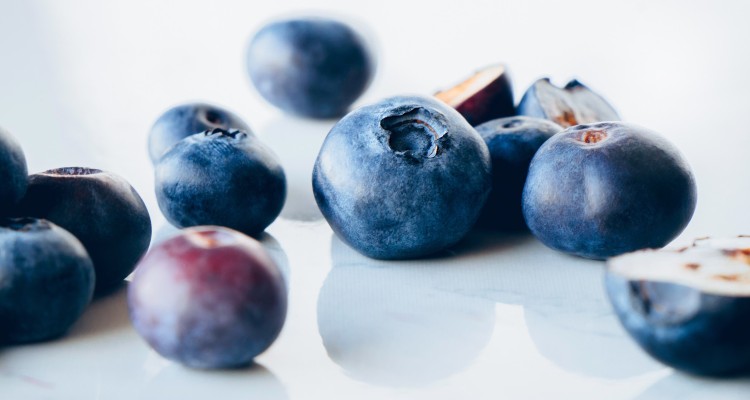
Blueberries and How they Can Impact Brain Health
Brain health may not be the first thing you think of when it comes to blueberries, but they contain several essential compounds that can help to boost cognitive function. Blueberries are often called a superfood and for good reason. These nutrient-dense berries contain a high level of antioxidants, helping to combat free radical damage and oxidative stress within the body.*
One reason that blueberries may impact brain health is that they’re loaded with flavonoids. Flavonoids are a broad set of phytonutrients found in most fruits and vegetables. Blueberries contain a unique class of beneficial flavonoids called anthocyanins, which also gives the berries their unique color.
Anthocyanins impart a deep red, purple or blue hue to various plant foods. Anthocyanins are found in high concentrations in foods such as blackcurrants, blackberries, eggplant, red cabbage, cranberries, cherries, and blueberries and act to protect the brain and nervous system from oxidative stress and inflammation, caused by free radical damage.* Similar to the nutrient citicoline, anthocyanins can cross the blood-brain barrier, which allows them to impart their protective effects on brain cells.*
Current research on blueberries demonstrates that they may help maintain critical thinking and memory by reducing inflammation, and inhibiting DNA damage in the brain.4 Anthocyanins in blueberries may also improve vascular function and blood flow which can impart protective effects on cognitive health.5* Blueberries, in particular, have been associated with benefits in memory and slowing cognitive decline.6 *
Blueberries can be included in the diet in their fresh, raw form, with organic varieties being the most nutrient-dense choice. Consuming just 1 cup of fresh blueberries is associated with improvements in cognition.7 If fresh blueberries are not an option, blueberry juice or blueberry nutritional supplements can be used as an alternative source.
Citicoline and Blueberries a Perfect Pair for Brain Health
Both citicoline and blueberries offer a variety of potential benefits for the brain.* They contain compounds that can help to provide stabilization in cell structure, which is critical to maintaining proper cell function.* They may also play a crucial role in modulating signaling pathways involved in inflammation, neurotransmission, and enhance neuroplasticity.8 They both provide essential free radical fighting support for the brain.*
Utilizing different pathways that lead to a similar outcome, citicoline and blueberries, are great ways to support brain health. Their neuroprotective effects may promote improved brain function, which can lead to greater longevity and optimal health.*
By Dr. Ramneek Bhogal

*These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any disease.
1"Secades JJ, Frontera G. CDP-choline: a pharmacological and clinical review. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 1995 Oct;17 Suppl B:1-54. Review. PubMed PMID: 8709678.
2"Fioravanti M, Yanagi M. Cytidinediphosphocholine (CDP-choline) for cognitive and behavioural disturbances associated with .... Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Apr 18;(2):CD000269. Review. PubMed PMID: 15846601
3"Parisi, V., Oddone, F., Ziccardi, L., Roberti, G., Coppola, G., & Manni, G. (2018). Citicoline and Retinal Ganglion Cells: Effects on Morphology and Function. Current neuropharmacology, 16(7), 919–932. https://doi.org/10.2174/1570159X15666170703111729
4 "Jie Wei, Guokun Zhang, Xiao Zhang, Dexin Xu, Jun Gao, Jungang Fan, and Zhiquan Zhou Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 2017 65 (29), 5973-5984 DOI: 10.1021/acs.jafc.7b02136
5 "Vauzour D, Camprubi-Robles M, Miquel-Kergoat S, Andres-Lacueva C, Bánáti D, Barberger-Gateau P, Bowman GL, Caberlotto L, Clarke R, Hogervorst E, Kiliaan AJ, Lucca U, Manach C, Minihane AM, Mitchell ES, Perneczky R, Perry H, Roussel AM, Schuermans J, Sijben J, Spencer JP, Thuret S, van de Rest O, Vandewoude M, Wesnes K, Williams RJ, Williams RS, Ramirez M. Nutrition for the ageing brain: Towards evidence for an optimal diet. Ageing Res Rev. 2017 May;35:222-240. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2016.09.010. Epub 2016 Oct 3. Review. PubMed PMID: 27713095"
6 "Bell L, Lamport DJ, Butler LT, Williams CM. A Review of the Cognitive Effects Observed in Humans Following Acute Supplementation with Flavonoids, and Their
seven.Associated Mechanisms of Action. Nutrients. 2015 Dec 9;7(12):10290-306. doi: 10.3390/nu7125538. Review. PubMed PMID: 26690214; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC4690090.
7." Miller MG, Hamilton DA, Joseph JA, Shukitt-Hale B. Dietary blueberry improves cognition among older adults in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlledtrial. Eur J Nutr. 2018 Apr;57(3):1169-1180. doi: 10.1007/s00394-017-1400-8. Epub 2017 Mar 10. PubMed PMID: 28283823
8.Subash, S., Essa, M. M., Al-Adawi, S., Memon, M. A., Manivasagam, T., & Akbar, M. (2014). Neuroprotective effects of berry fruits on neurodegenerative .... Neural regeneration research, 9(16), 1557–1566. https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.139483